Page 226 - Spirit and Mind. Vol 1
P. 226
Nicolai Levashov. Spirit and mind. Vol.1
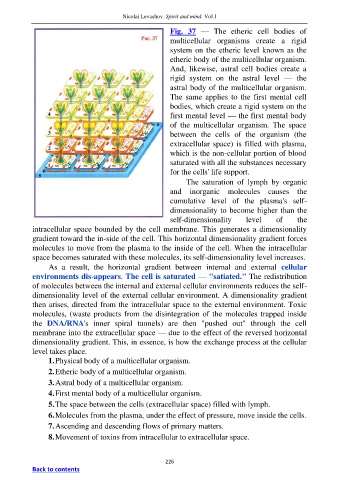
Fig. 37 — The etheric cell bodies of
multicellular organisms create a rigid
system on the etheric level known as the
etheric body of the multicellular organism.
And, likewise, astral cell bodies create a
rigid system on the astral level — the
astral body of the multicellular organism.
The same applies to the first mental cell
bodies, which create a rigid system on the
first mental level — the first mental body
of the multicellular organism. The space
between the cells of the organism (the
extracellular space) is filled with plasma,
which is the non-cellular portion of blood
saturated with all the substances necessary
for the cells' life support.
The saturation of lymph by organic
and inorganic molecules causes the
cumulative level of the plasma's self-
dimensionality to become higher than the
self-dimensionality level of the
intracellular space bounded by the cell membrane. This generates a dimensionality
gradient toward the in-side of the cell. This horizontal dimensionality gradient forces
molecules to move from the plasma to the inside of the cell. When the intracellular
space becomes saturated with these molecules, its self-dimensionality level increases.
As a result, the horizontal gradient between internal and external cellular
environments dis-appears. The cell is saturated — "satiated." The redistribution
of molecules between the internal and external cellular environments reduces the self-
dimensionality level of the external cellular environment. A dimensionality gradient
then arises, directed from the intracellular space to the external environment. Toxic
molecules, (waste products from the disintegration of the molecules trapped inside
the DNA/RNA's inner spiral tunnels) are then "pushed out" through the cell
membrane into the extracellular space — due to the effect of the reversed horizontal
dimensionality gradient. This, in essence, is how the exchange process at the cellular
level takes place.
1. Physical body of a multicellular organism.
2. Etheric body of a multicellular organism.
3. Astral body of a multicellular organism.
4. First mental body of a multicellular organism.
5. The space between the cells (extracellular space) filled with lymph.
6. Molecules from the plasma, under the effect of pressure, move inside the cells.
7. Ascending and descending flows of primary matters.
8. Movement of toxins from intracellular to extracellular space.
226
Back to contents